Mortality factors linked to diet 🥗
According to a study based on global mortality statistics from 195 countries between 1990 and 2017, the five dietary factors that most decrease life expectancy both in Europe and globally are:
- Diet low in whole grains
- High sodium diet
- Low fruit diet
- Low nut diet
- Diet low in vegetables
According to a study of 6381 people, the prevalence of cancer is up to four times higher in people with diets high in animal protein (more than four times higher in people with diets low in animal protein). four times higher in people with diets high in animal protein (more than 20% of daily calories than in people 20% of daily calories) than in people with diets low in animal protein (less than 10% of daily calories). The same effects were not observed with high levels of vegetable protein.
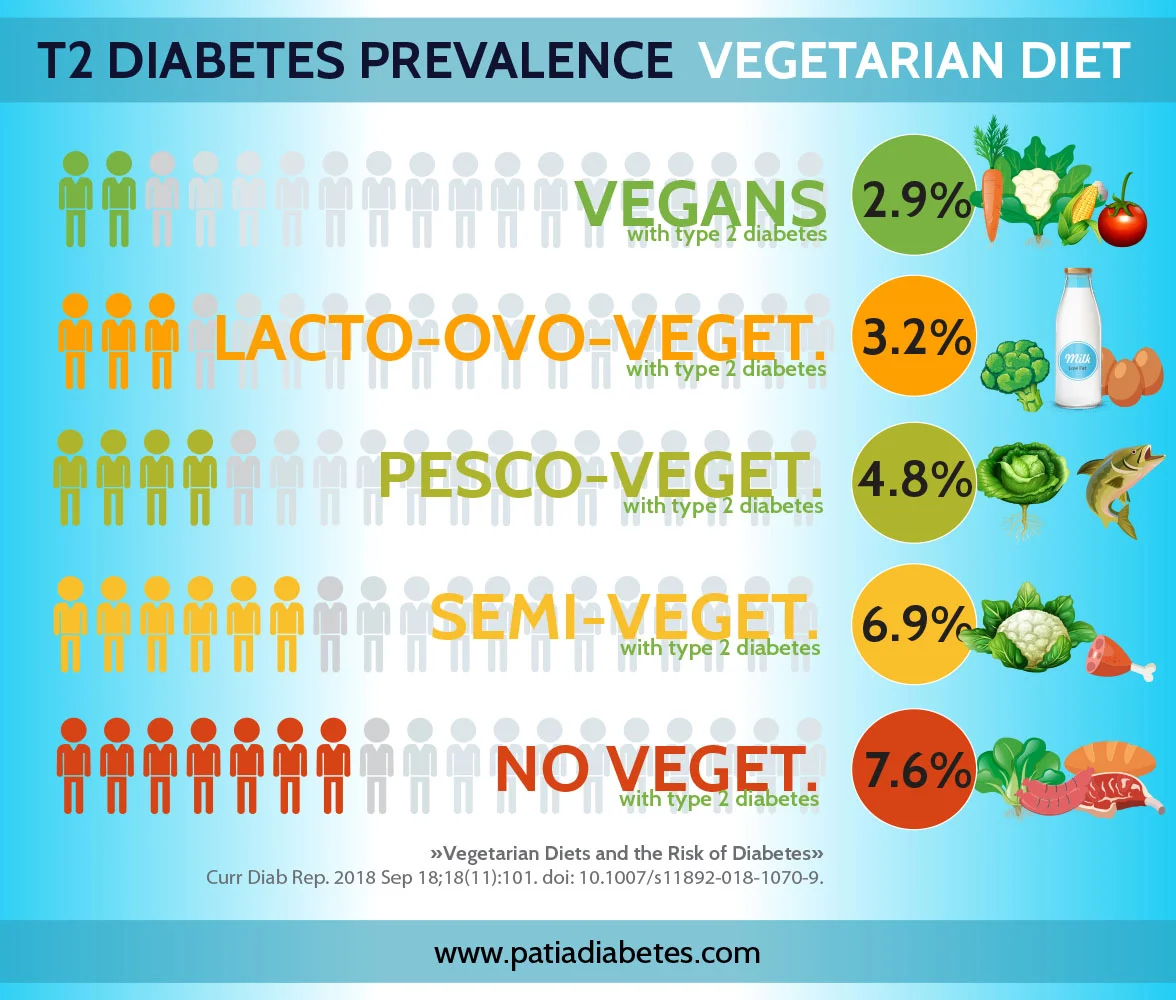
A plant-based diet is associated with lower cholesterol and triglyceride levels compared to an omnivorous diet.
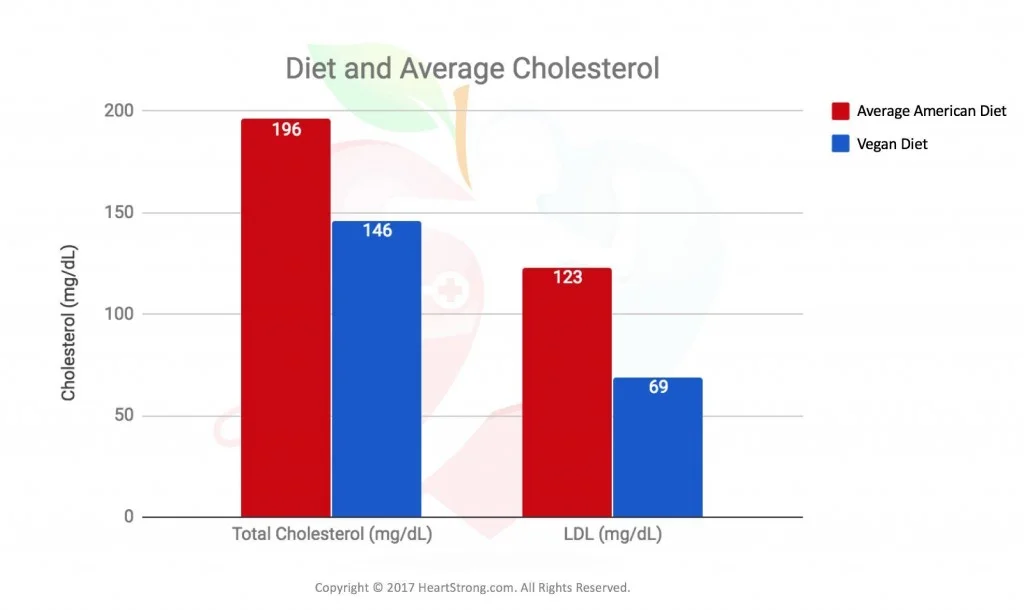
Longer life expectancy 
A study carried out in California between 2002 and 2007 with 96,000 participants will find that the average life expectancy of men following a 100% plant-based diet was found that the average life expectancy of men following a 100% plant-based diet was 9.5 years longer than that of men following an omnivorous diet (83.3 vs 73.8 years). 9.5 years longer than that of men on an omnivorous diet (83.3 vs 73.8 years). The difference was somewhat less marked in the female participants, with a life expectancy 6.1 years higher in women than in men. life expectancy 6.1 years higher in those following a plant-based diet (85.7 vs 79.6 years).
Using data from the same study, the protein intake of people with omnivorous, vegetarian and vegan diets was vegetarian and vegan diets, with similar results in all three: 74.7, 70.6 and 70.7 grams per day, respectively. In all three cases, the recommended daily amount of 46 g for an average woman and 56 g for an average man, the widespread belief that plant-based diets do not provide enough protein.
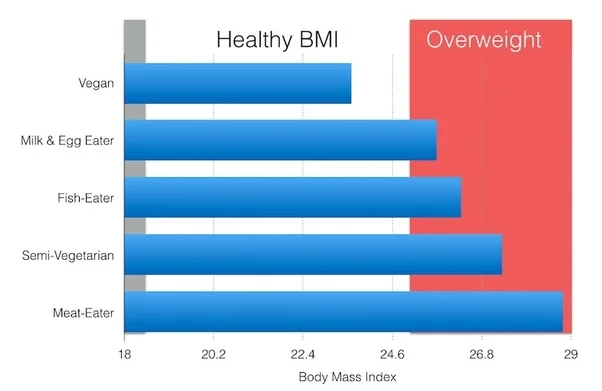
On the other hand, 70.6% of omnivores had a body mass index above 25, the threshold for overweight, compared to 49.7% of vegetarians and only 33.1% of vegans.
A diet for every stage of life 
The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics of the United States, the organization with the most professional nutritionists in the world, affirms that 100% plant-based diets are suitable for any stage of life, including infancy and pregnancy. On the other hand, The American Journal of Cardiology recommends a 100% plant-based diet to prevent arteriosclerosis and reduce the risk of cancer and other chronic diseases.
Sources 🔤
1. Health effects of dietary risks in 195 countries, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017- Afshin et al, 2019
2. Low Protein Intake Is Associated with a Major Reduction in IGF-1, Cancer, and Overall Mortality in the 65 and Younger but Not Older Population- Levine et al. 2014
3. Vegetarian Diet and Cholesterol and Triglycerides Levels- De Biase et al, 2005
4. The Garden of Eden—plant based diets, the genetic drive to conserve cholesterol and its implications for heart disease in the 21st century- Jenkins et al, 2002
5. Vegetarian diets in the Adventist Health Study 2: a review of initial published findings- Orlich et al, 2014
6. Nutrient Profiles of Vegetarian and Non Vegetarian Dietary Patterns- Rizzo et al, 2014
7. Position of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics: Vegetarian Diets- Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, 2016
8. Introduction: More Than Coronary Artery Disease- Esselstyn et al, 1998
To find out more 🔍
- Brief introductory guide to plant food
- Youtube channel: NutritionFacts.org
- How Not to Die
- How not to diet
- Becoming Vegan